Experimental low-profile aircraft "Have Blue" - the forerunner of the F-117
The first who developed and began to apply RPM - Nazi Germany in the last years of the war:
- 1944 year - diesel hulls and submarine periscopes for the first time cover RPM;
- 1945 year - it was supposed to cover the RPM fighter "No.IX". Serial fighters would get a trim soaked in RPM.
After the Second World War aviation equipment began to develop rapidly (mainly due to German developments). High-speed rocket and jet engines are being created. They do not pay much attention to radar signature due to the predominance of high speeds. Development, of course, is underway, but mainly in addition to the existing capabilities of the aircraft.
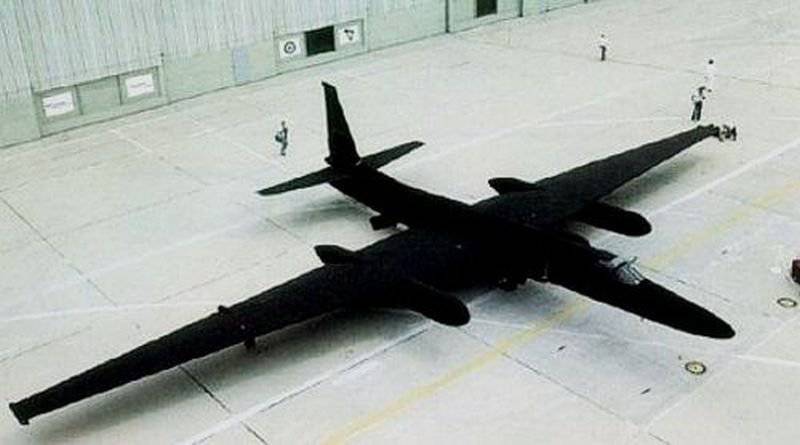
Here you can mention the work of the American designer “Clarencel (Kelly) Jonson” when creating the reconnaissance high-altitude aircraft “Lockheed U-2”, Soviet designers from the design bureau V.Myasischev when creating the strategic bomber 3M.

At the beginning of the second half of the 21 century, with the development of air defense systems in the Soviet Union and the United States, provided with modern radar and missiles, hitting targets at high altitudes, reducing and reducing radar visibility goes into the priorities and requirements when creating aircraft.
The main way to deal with enemy radars for aircraft was to lower at low altitudes. This immediately reduced the combat readiness of the aircraft - rapid fuel consumption, fatigue of the crew, the impact of unnecessary loads on equipment, units and weapons.
The main idea is to fly at a given altitude (high and medium altitudes) above enemy territory covered by air defense weapons. In addition, performing flights, equipment and weapons of the aircraft, it is designed to work precisely at given altitudes. That is why the reduction of the radar visibility becomes a priority in the development of military aviation.
The first to significantly reduce the radar visibility of the American designers tried to create the "Lockheed SR-71" - supersonic altitude reconnaissance. The very layout of the aircraft has already led to a decrease in radar visibility. In addition, the company developed a radio absorbing structure filled with a honeycomb plastic filler, which was installed at different inner ends of the case. RP-design was tested on the prototype aircraft (A-12). The first SR-71 of the year has risen to the sky. RPM was installed in the toes of the wing and in elevons. Outside, the entire structure of the aircraft is covered with a special paintwork, which lowers the temperature characteristics of the skin when flying at cruising altitude. The paint, created on the basis of ferrite mixtures, reduced the overall radar visibility of the reconnaissance plane, evenly reflecting electromagnetic waves. Note that compared to the first operating time on the Lockheed U-22.12.1964, the reconnaissance aircraft already had almost half the radar visibility.

The following work in the United States was under the "pressure" of the Soviet anti-aircraft missile systems C-75 / 125. Their use in a number of countries in the Middle East and in the military conflict in Vietnam was an unpleasant surprise for the United States military. The REP equipment installed on American aircraft turned out to be ineffective against them, the REP equipment itself, “took over” a good part of the payload. The development of a decrease in radar visibility occurs at the beginning of the 1970s. In the United States, they first created the civilian version of the Eagle, and a little later, the military version of the YE-5A aircraft (prototype), with a fiberglass skin and extensive use of RPM in the internal structure.

It is the tests of this sample with the installed piston engine that give rise to the program for creating an inconspicuous fighter with a jet engine. In the 1973 year, DARPA and the United States Air Force issue a design task for an inconspicuous fighter. Practically all “heavy” airlines of America responded to it. The company "Lockheed" did not get the job, because more than a decade was not engaged in the creation of fighters. But she sent her project for consideration to DARPA. In 1975, she and Northrop were selected for the XST project - an experimental technique of low visibility. In Lockheed, the development of this technology is entrusted to the advanced development department, which, in fact, created the U-2 and SR-71 aircraft.
Basic requirements for creating an aircraft with "XST":
- the use of new solutions in the application of low-reflective forms;
- the creation of aircraft design, primarily based on the reduction of X-ray visibility, and after the aerodynamic characteristics;
- maximum decrease in radar visibility;
At that time, thanks to the rapid growth of technology, it was already known about the most powerful reflectors of radio waves. They were called mirror points, with accurate reflection of the radio wave in the opposite direction. Surface joints were studied, a number of which acted as a reflector. The required low reflector airframe should have an integral layout with the minimum possible number of protruding and sharp parts of the structure.
Theoretically, the most suitable glider for this aircraft should have been a glider built according to the “flying wing” scheme. It initially has a minimum number of sharp and protruding surfaces and smooth lines. “Live” examples are the American Northrop YB-49 bomber and the English Vulcan bomber.
But the designers of both companies, having calculated the value of the EPR, come to the conclusion that the tailless type with facet shape is best suited for an inconspicuous aircraft. And although using this scheme, the body would have bright points, but if properly selected flat surfaces, their number would be reduced to a minimum, and the use of a facet shape would reduce the level of the reflected signal, and the plane would become almost unnoticeable on the enemy radar.
Both presented projects were very similar to each other:
- facet body;
- wing with a large sweep;
- two-fin plumage;
- shielding nozzles used engines.
The main difference was the location of the air intakes. The designers from Northrop installed one air intake above the fuselage, the designers from Lockheed installed two air intakes on the sides.
The first stage of the XST program required the creation of large-scale models for an overall assessment of the EPR. Scale models - 1: 3. Trials begin in 1976 and ended with a win from Lockheed. She receives a contract to create two experimental samples. They are created by a program called "Have Blue".
The most surprising is the recognition of one of the engineers at Lockheed that the success of their project was largely due to the use of the work of the Soviet theorist P. Ufimtsev, who proposed using the mathematical apparatus for EPR calculations in a published article. This mathematical apparatus was used in the American company for calculating the EPR of various bodies. He helped to reduce all the costs of creating the aircraft according to the “Have Blue” program by at least 30 percent (later on, the calculations were used to create the F-117). The models of the new aircraft flew around 2000 hours before the optimal configuration was chosen. It was used to create a full-scale radar model, which worked out all the details of the aircraft. All this helped the designers in a short time to create two prototypes.
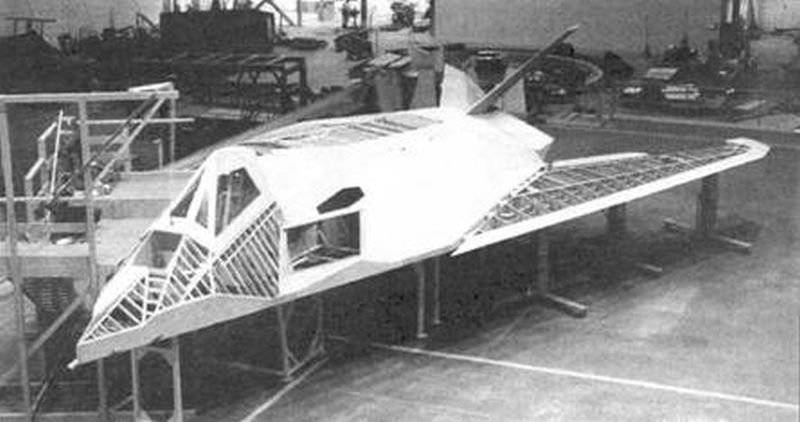
Prototype "Have Blue"
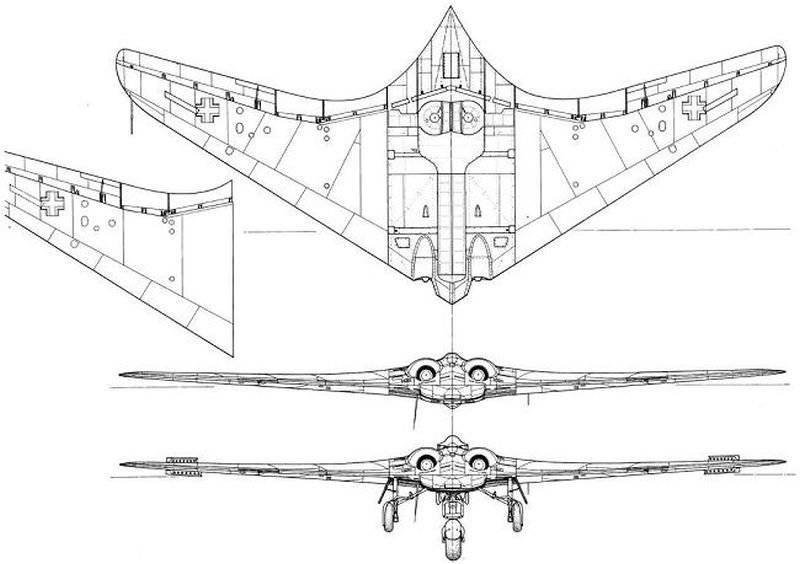
The plane itself turned out to be small, the full length of the 14.4 meter. It installed two engines "J85-GE-4A" from the company General Electric. Such engines were equipped with the North American T-2В deck training aircraft. Flap and air brakes on the prototype was not, as they immediately raised the EPR. Control was carried out using simple elevons and two full-turning carinae. The entire aircraft structure was assembled from aluminum using titanium and steel in the most heat-stressed points. Piloting was carried out by one pilot with the help of a handle and pedals. The signals from them came to the radio remote control system. When creating the aircraft abandoned the mechanical duplication of the control system. The maximum weight of the prototype machine did not exceed 5.7 tons, of which 1.6 tons was fuel.
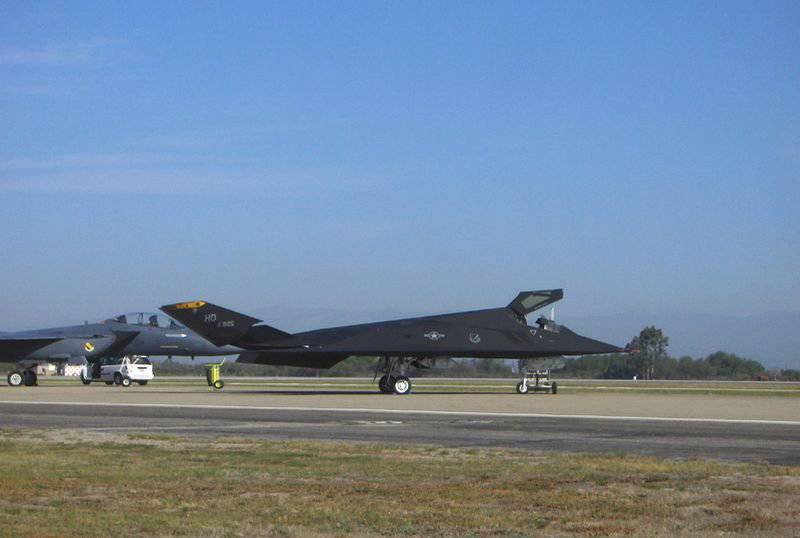

First, the plane began to work out the motor system on the ground. The aircraft was highly classified, the main engine tests were carried out at night from the 4.11.1977 year. After they ended, the plane was dismantled and taken to a secret air base in Groom Lake.
1.12.1977, the first of the experimental aircraft "Have Blue" (number 1001) rises into the sky under the control of test pilot K.Dyson. It began to work out the controllability of the aircraft and study the characteristics of stability. He managed to make 36 departures, when 4.04.1978, the aircraft jammed right support. The pilot unsuccessfully tried to “peep” the support by making various attempts. However, nothing came of it. K.Dyson makes a decision - having gained altitude about 3 kilometers and having exhausted all the fuel, it catapults.
The second prototype (number 1002), for the first time rose in the sky 20.07.1978 of the year. Used to study the characteristics of the aircraft’s X-ray visibility. During the year of operation 52 made the departure and successfully completed the test.
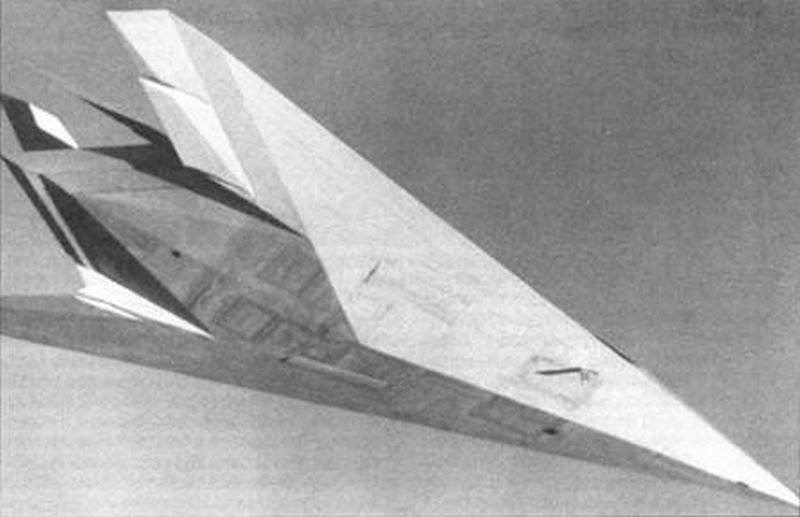
At the end of the test, the real X-ray visibility of the aircraft was tested. The plane tried to detect the existing means of air defense and radar. As a result, the commission noted the successful low radar visibility of the aircraft in all scanned ranges. He became the forerunner of future subtle warplanes. The total cost of creating two aircraft - 37 million dollars.
Key Features:
- Length - 14.4 meters;
- height - 2.3 meters;
- wing - 6.86 meter;
- weight empty / max 4 / 5.7 tons;
- characteristics of thrust of one engine - 1338 kgf;
- cruiser / normal speed - 456 / 966 km / h;
- flight time about an hour;
- kilometer high altitude 10.2;
- crew - 1 pilot.
Information sources:
http://lib.rus.ec/b/201985/read
http://www.airwar.ru/enc/xplane/haveblue.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lockheed_Have_Blue
Information